Customer Data Security in Call Centers: Best Practices for Compliance
Call centers handle a wealth of sensitive customer information daily, making data security a top priority.
Sept. 22, 2023, 3 min read,

In an era defined by connectivity and digital transformation, the Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a transformative force, shaping the way we interact with the world around us. At its core, IoT is all about connecting everyday objects and devices to the internet, creating a vast ecosystem that promises to make our lives more convenient, efficient, and data-driven. In this article, we'll explore the profound impact of IoT on networking and how it is revolutionizing industries and the way we live.
IoT refers to the interconnection of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and even entire buildings through the internet. These "smart" devices are embedded with sensors, software, and network connectivity, enabling them to collect and exchange data. The goal is to enhance efficiency, automation, and decision-making in various applications, from industrial processes to our homes.
IoT encompasses a wide range of devices and applications, including:
From thermostats and lighting systems to voice-activated assistants, IoT devices are making homes more energy-efficient and user-friendly.
In industries like manufacturing and agriculture, IoT sensors and machinery optimize production processes, monitor equipment health, and reduce downtime.
IoT enables real-time monitoring of vehicles, leading to improved safety, navigation, and predictive maintenance in the automotive sector.
IoT-powered wearables and medical devices track vital signs, deliver medication reminders, and allow remote patient monitoring.
IoT technologies enhance urban planning, traffic management, waste management, and energy efficiency in cities worldwide.
IoT's rapid growth and adoption have significant implications for networking:
IoT devices are expected to proliferate into the billions. Networking infrastructure must scale to accommodate this massive increase in connected devices.
Many IoT devices operate on battery power and require low-power, long-range networking solutions like LoRaWAN and NB-IoT.
To reduce latency and process data closer to the source, IoT networks are increasingly incorporating edge computing capabilities.
With numerous devices connected to networks, security becomes a paramount concern. Protecting IoT devices and data from cyber threats is a top priority.
The data generated by IoT devices can be vast and diverse. Efficient data management and analytics are crucial for deriving meaningful insights.
IoT optimizes processes, reduces waste, and enhances resource management, leading to increased operational efficiency.
Predictive maintenance and remote monitoring of equipment reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
Data from IoT devices provides real-time insights, enabling smarter, data-driven decisions.
Smart homes, wearable devices, and IoT-powered services create more convenient and personalized experiences.
IoT can contribute to sustainability efforts by optimizing resource usage and reducing energy consumption.
The Internet of Things is reshaping the way we interact with our surroundings, from our homes to our workplaces and cities. As IoT continues to grow, networking technologies must evolve to meet the demands of this connected world. The combination of IoT and advanced networking promises to create a smarter, more efficient, and more interconnected world, bringing us closer to the vision of a truly "smart" future.
Call centers handle a wealth of sensitive customer information daily, making data security a top priority.

With the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI), companies are finding innovative ways to revolutionize their customer feedback services

Embracing Technology for Enhanced Patient Care

Customer service is not just about solving problems and answering questions; it's also about understanding human psychology and emotions. Call centers are at the forefront of this intricate interaction, where every conversation can impact customer satisfaction. In this article, we delve into the psychology of customer service and how call centers can harness it to leave customers delighted.

In this article, we'll explore the key strategies that can transform your training program and empower call center agents to excel in their roles.

Branch connectivity is a crucial aspect of modern business operations...

In this article, we'll explore the pros and cons of each approach to help businesses make an informed choice.

In this article, we will delve into the crucial role of DNS in the internet, its function, and its significance in simplifying our online experience.

Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP). what you should know about it.

Do you need to install a server in your place or do you need outsourcing?

Technical services for installing and setting up servers and supporting servers such as HP and Dell at your' place

video surveillance setups, CCTV gear with setup and installtion services.

In today's globalized business landscape, powerful communication and customer service are vital for achievement.

One question many business owners often wonder is whether they need a call center solution.

It's crucial to understand the essential software and equipment required to set up a call center. In this article, we'll walk you through the key components you need to establish a functional call center.

IPv4 vs. IPv6: Navigating the Transition to the New Internet Protocol

In today's world, fast internet is important. There are two common ways to get it: Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) and Digital Subscriber Line (DSL).

Acronyms like DSL and VDSL often leading to confusion about their meanings and capabilities. Are they the same thing? Or do they represent distinct technologies?

In this article, we'll dive into the world of call center performance measurement and explore the critical metrics that drive success.

"This has been by far the worst airline call center experience I've ever had"

Explore the latest advancements in access control technology, from IoT integration and touchless entry to biometric authentication and AI-driven automation, ensuring robust and efficient security solutions for modern workplaces.

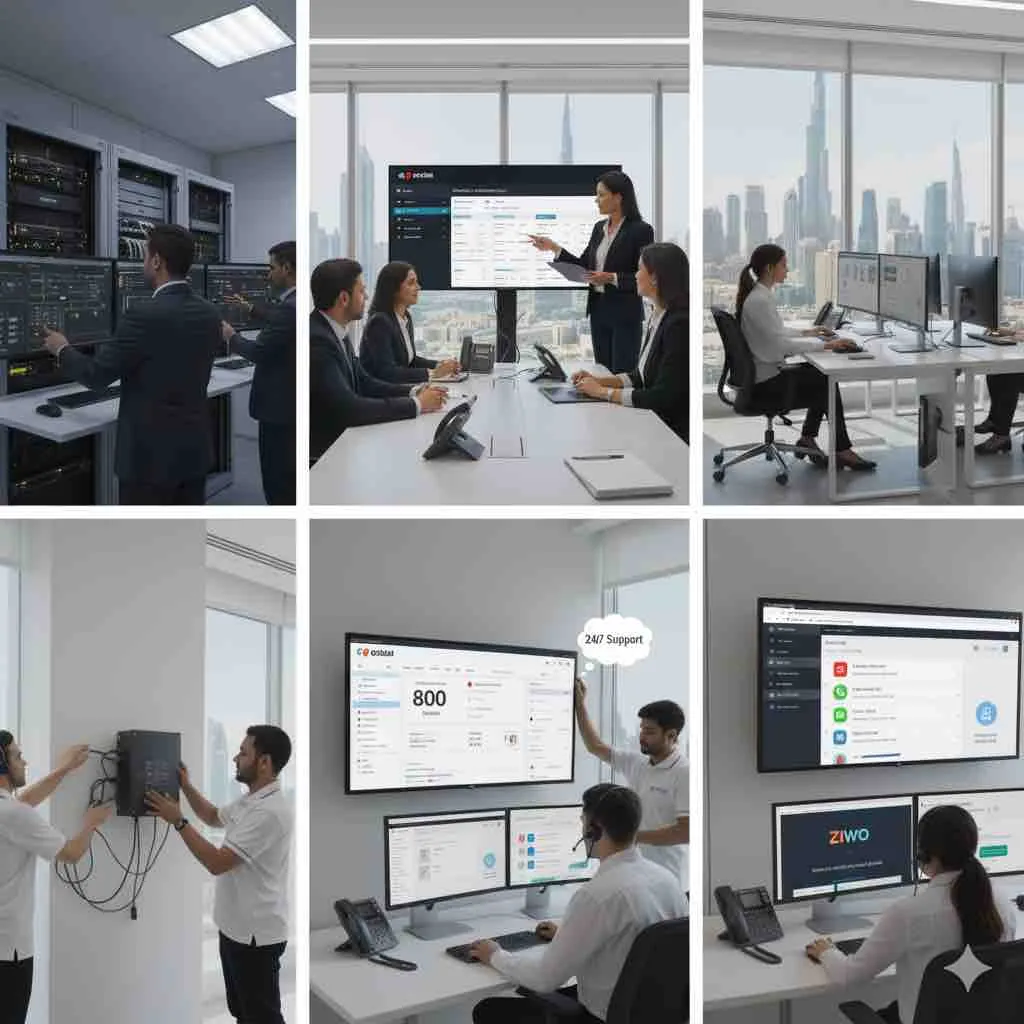
In a fast-paced digital world, where communication and technology are vital, ArcNet stands as your reliable partner for all your IT and Telecom needs.

Enhance your business communication with ArcNet’s cutting-edge Call Center Solutions in Dubai, UAE. From advanced software to customized projects, we empower businesses with scalable, efficient, and cost-effective call center services tailored for success.

Discover how custom IT applications are reshaping the landscape of education, fostering innovation, accessibility, and collaboration.

Deliver exceptional customer service and improve agent efficiency with our Call Center Solution, available on-premise or in the cloud

Structured cabling refers to the standardized, organized, and comprehensive cabling system that serves as the foundation for all communication networks within a building or campus....

Building connections that matter — discover how to set up a powerful call center in Dubai with the right technology, people, and local expertise
Here’s a simple breakdown of on-premise vs. cloud contact centers — setup time, costs, scalability, and compliance tips to help you choose what fits your business best.

Find the perfect call center setup for your Dubai business — scalable, bilingual, and built for UAE success with ArcNet.
